Course Design By
Nasscom & Wipro
+ More Lessons
Course Design By
Nasscom & Wipro
Course Offered By
Croma Campus
Stories
success
inspiration
career upgrade
career upgrade
career upgrade
career upgrade
21-Feb-2026*
23-Feb-2026*
25-Feb-2026*
21-Feb-2026*
23-Feb-2026*
25-Feb-2026*
You will get certificate after
completion of program
You will get certificate after
completion of program
You will get certificate after
completion of program
in Collaboration with

Empowering Learning Through Real Experiences and Innovation
we train you to get hired.
Phone (For Voice Call):
+91-971 152 6942WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
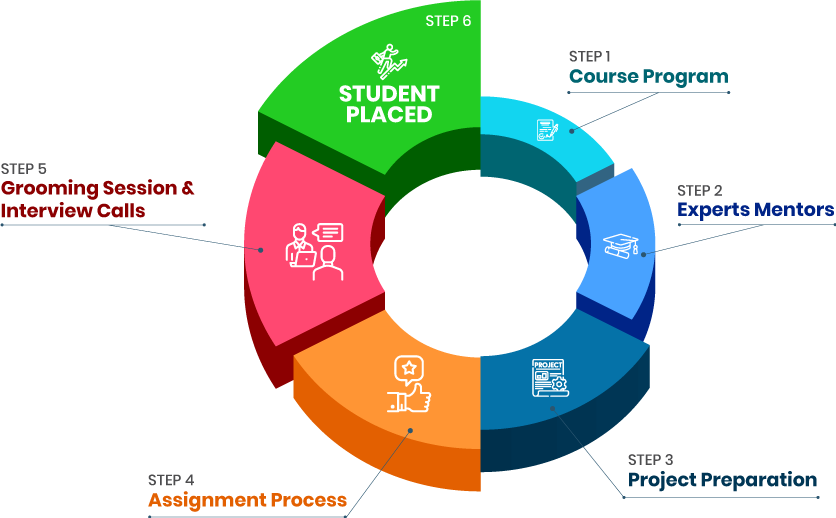
+91-971 152 6942Get a peek through the entire curriculum designed that ensures Placement Guidance
Course Design By
Course Offered By
Ready to streamline Your Process? Submit Your batch request today!
Highest Salary Offered
Average Salary Hike
Placed in MNC’s
Year’s in Training

fast-tracked into managerial careers.
Get inspired by their progress in the
Career Growth Report.
FOR QUERIES, FEEDBACK OR ASSISTANCE
Best of support with us
For Voice Call
+91-971 152 6942For Whatsapp Call & Chat
+91-9711526942