Course Design By
Nasscom & Wipro
Starting at
Register Now
And Get
10%
OFF
Limited Time Offer*
Introduction To Python
Python Keyword and Identiers
Introduction To Variables
Python Data Type
Control Structure & Flow
List
Tuple
Dictionary
Sets
Strings
Python Function, Modules and Packages
Decorator, Generator and Iterator
Python Exception Handling
Python File Handling
Memory management using python
Python Database Interaction
Reading an excel
Complete Understanding of OS Module of Python
Data Analysis and Visualization using Pandas.
Data Analysis and Visualization using NumPy and MatPlotLib
Introduction to Data Visualization with Seaborn
Introduction to Statistics
EDA (Exploratory Data Analysis)
Data Pre-Processing & Data Mining
Introduction to Predictive Modelling
SQL Server Fundamentals
SQL Server 2019 Database Design
SQL Tables in MS SQL Server
Data Validation and Constraints
Views and Row Data Security
Indexes and Query tuning
Stored Procedures and Benets
System functions and Usage
Triggers, cursors, memory limitations
Cursors and Memory Limitations
Transactions Management
Understanding Concepts of Excel
Ms Excel Advance
MIS Reporting & Dash Board
What is Macro
Recording a Macro
Different Components of a Macro
What is VBA and how to write macros in VBA.
Introduction to Power BI
Power BI Desktop
Power BI Data Transformation
Modelling with Power BI
Data Analysis Expressions (DAX)
Power BI Desktop Visualisations
Introduction to Power BI Dashboard and Data Insights
Direct Connectivity
Publishing and Sharing
Refreshing Datasets
Introduction to Machine Learning
Time Series Analysis
Statistical Foundations (Self-Paced)
Introduction to Text Mining and NLP
Introduction to Deep Learning
Deep Learning Networks
Capstone Project
Course Design By

Nasscom & Wipro
Course Offered By

Croma Campus
You will get certificate after completion of program
.png)
Numpy

Python
.png)
Power BI
.png)
Panda

Start your journey with the best IT
training experts in India.

50% Average Salary Hike
Course : Data Science

Course : Data Science


Course : Data Science


Course : AI


You will get certificate after
completion of program

You will get certificate after
completion of program

You will get certificate after
completion of program
Get a peek through the entire curriculum designed that ensures Placement Guidance
Course Design By


Course Offered By

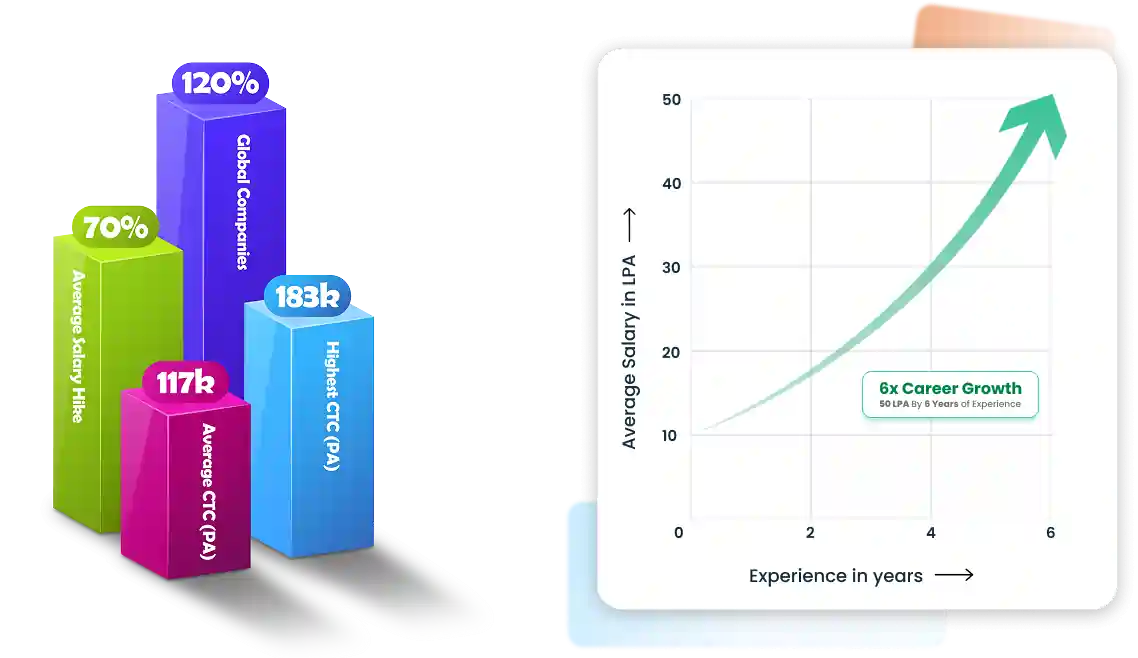
*Insights Displayed Are as Per Our Recorded Data
Data Scientist ₹6L - ₹16L
Machine Engineer ₹7L - ₹11L
AI Developer ₹7L - ₹10L
ML Engineer ₹8L - ₹13L
AI Analyst ₹6L - ₹9L
AI Consultant ₹8L - ₹12L
Deep Specialist ₹8L - ₹14L
AI Researcher ₹9L - ₹15L
NLP Engineer ₹8L - ₹12L
Bot Developer ₹6L - ₹9L
Risk Analyst ₹7L - ₹11L
Data Consultant ₹9L - ₹15L
Statistician Expert ₹5L - ₹9L
Data Architect ₹8L - ₹10L
Technical Analyst ₹5L - ₹8L
Technical Analyst ₹5L - ₹8L
Data Architect ₹8L - ₹10L
Statistician Expert ₹5L - ₹9L
Data Consultant ₹9L - ₹15L
Risk Analyst ₹7L - ₹11L
Bot Developer ₹6L - ₹9L
NLP Engineer ₹8L - ₹12L
AI Researcher ₹9L - ₹15L
Deep Specialist ₹8L - ₹14L
AI Consultant ₹8L - ₹12L
AI Analyst ₹6L - ₹9L
ML Engineer ₹8L - ₹13L
AI Developer ₹7L - ₹10L
Machine Engineer ₹7L - ₹11L
Data Scientist ₹6L - ₹16L

*Image for illustration only. Certificate subject to change.
Our Master program is exhaustive and this certificate is proof that you have taken a big leap in mastering the domain.
The knowledge and skill you've gained working on projects, simulation, case studies will set you ahead of competition.
Talk about it on Linkedin, Twitter, Facebook, boost your resume or frame it- tell your friend and colleagues about it.

Total Exam Submitted
Best of support with us
The data science professional training program will help you master the key skills that are necessary for becoming an expert in data science. In this course, you will learn about ML, DL, statistics, python, etc. Moreover, you will learn to develop data models for analyzing data and extracting useful/meaningful insights. You will also become proficient in performing linear and logistic regression and cluster & factor analysis. After completing the data science professional training program, you may get various types of job opportunities in big organizations. For example, you may get an opportunity to work as an:

There is a huge demand for competent data science professionals in the market. Students who complete the data science professional training program may get various types of roles and jobs in an organization. This is because of the benefits that a data science professional provides to a company or organization. This is why many organizations are more than happy to give big paychecks to data science professionals for their services.
The demand for data science professionals is increasing in the market with every passing day. This is because of the benefits that an organization gets from the service of a data scientist. By joining this course, you will acquire all the skills that are essential/important for becoming an expert data science professional. Furthermore, you will learn to develop data models for analyzing data and extracting useful/meaningful insights.
![]() With project-based training under an expert data scientist, you will acquire all the skills that a competent data scientist must have.
With project-based training under an expert data scientist, you will acquire all the skills that a competent data scientist must have.
![]() Students who join the data science professional training program can guarantee themselves a fulfilling and successful career as a data science professional. Moreover, you will earn a hefty remuneration as a data scientist. On average, a data scientist can earn around ₹6,00,000-₹22,00,000 PA.
Students who join the data science professional training program can guarantee themselves a fulfilling and successful career as a data science professional. Moreover, you will earn a hefty remuneration as a data scientist. On average, a data scientist can earn around ₹6,00,000-₹22,00,000 PA.
![]() As per a survey, the data science industry will create around 11.5 million jobs by the year 2026.
As per a survey, the data science industry will create around 11.5 million jobs by the year 2026.
The data science professional training program aims to provide quality data science education to aspiring data scientists and make them experts in working with data. Additionally, you will learn to work with various data collection and data visualization tools and software.
Things you will learn:
The main objective of the data science professional training program is to make aspiring data experts competent data scientists. The course covers all the concepts and skills that a skilled data professional must master. The training program fulfills the emerging demands of the data science industry and is developed in partnership with working data science professionals.
For Voice Call
+91-971 152 6942For Whatsapp Call & Chat
+91-9711526942