Course Design By
Nasscom & Wipro
Learning out the intricacies involved in spring boot.
Going throughout the facets of Angular.
Handling out the intricacies involved in Spring boot.
Developing multiple Full Stack projects.
One-to-one handling experience of procedures.
Core Java- In this module, you will be learning the foundation of Java programming. Along with this, you will also learn the syntax, data types, variables, operators, control flow statements, and basic object-oriented concepts.
Object- Oriented Programming (OOP) Concepts- Here, you will be learning the fundamental principles of OOP. This will include inheritance, polymorphism, e
Java Collections Framework- In this module, you will be learning a set of interfaces and classes for storing and manipulating collections of objects. Along with this, you will also learn lists, sets, maps, and queues.
Java Exception Handling- Here you will be learning how to handle the errors and exceptions in Java programs. Along with this, you will also be able to use try-catch blocks to catch exceptions and prevent program crashes.
Java Input/Output (I/O)- This course will help you understand how to read and write data to files, streams, and other sources. Furthermore, you will also be able to use classes like File, FileReader, FileWriter, and BufferedReader for I/O operations.
Multithreading and Concurrency- Explore how to create and manage multiple threads of execution in Java. Along with this, you are also going to learn about thread synchronization, deadlocks, and concurrent programming techniques.
Java Streams API- It refers to a powerful API introduced in Java 8 useful for functional-style programming. Using it allows you to process collections of data efficiently using lambda expressions and method chaining.
Java 8 Features- This is useful for exploring the new features introduced in Java 8, such as lambda expressions, method references, streams, and default methods for interfaces.
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC)- This is a popular Java API useful for connecting to and interacting with databases. Along with this, the JDBC is useful for executing SQL queries, retrieving data, and updating database records.
Java Servlets- This refers to the server-side components that are useful for handling the requests and generating responses. Along with this, they are also useful for building web applications and dynamic content.
JavaServer Pages (JSP)- It is a popular technology useful for creating dynamic web content. Along with this, it also combines the HTML, JSP tags, and Java code to generate dynamic web pages.
Spring Framework- It is a comprehensive framework for building enterprise-level Java applications. Using this solution provides you with the tools for dependency injection, data access, web development, and more.
Spring Boot- This is a simplified version of Spring Framework that offers rapid application development and configuration. Along with this, it provides a quick start for building Spring-based applications.
Spring MVC- It refers to a popular module within the Spring Framework for building web applications. Using this module provides you with a Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture for separating concerns.
Spring Data JPA- This is a popular data access framework that simplifies database interactions. Along with this, it provides users with a repository abstraction layer and query methods.
Hibernate ORM- It is a popular object-relational mapping (ORM) framework for Java. Along with this, it also maps Java objects to database tables for easier data persistence.
RESTful Web Services- These are useful for designing and developing web services using RESTful principles. Along with this, you will also be able to create APIs for communication between different applications.
Microservices Architecture- The Microservices architecture is useful for breaking down applications into smaller, independent services. Along with this, it improves the overall scalability, maintainability, and resilience.
API Gateway and Security- This solution helps in implementing an API gateway to manage API traffic and security. Along with this, it also helps in implementing authentication, authorization, and rate limiting.
Front-End Technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript)- Java developers often need to work with front-end technologies to build complete web applications. This helps in understanding the HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for creating user interfaces.
Angular/React- This is a popular JavaScript framework useful for building dynamic user interfaces. Along with this, it can also be used in conjunction with Java for full-stack web applications.
Bootstrap- It refers to a popular CSS framework useful for creating responsive and mobile-friendly designs. Along with this, it can also be used with Java-based web applications.
Thymeleaf- It is a popular Java template engine for creating dynamic HTML content. Along with this, it is useful in Spring MVC applications.
Version Control (Git)- This is a popular tool for tracking changes to code and collaborating with other developers. Along with this, it is essential for managing Java projects.
Build Tools (Maven/Gradle)- These tools are useful for conducting the automation tools for building, testing, and deploying Java applications. It is useful for simplifying the development and deployment process.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)- It refers to a set of practices for automating the building, testing, and deployment of applications. Along with this, it also improves the overall software quality and delivery speed.
Docker and Containerization- Here you will be understanding the Docker for creating and managing containers. Along with this, you will also learn how to use Docker to package applications and their dependencies for consistent deployment.
Unit Testing (JUnit, Mockito)- Here you will be writing the unit tests to ensure code quality and maintainability. Along with this, you will also learn the frameworks like JUnit and Mockito for effective testing.
Integration Testing- You will test how different components of an application work together. Alog with this, you will be able to identify and address integration issues.
Cloud Deployment (AWS, Azure)- You will be able to deploy Java applications to cloud platforms like AWS or Azure. Along with this, you will be able to leverage cloud services for scalability, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
Database Management (SQL, NoSQL)- Here you will be working with relational databases (SQL) or NoSQL databases. Furthermore, you will also be able to use SQL for querying and manipulating data in relational databases.
Project Work/Capstone Project- You will be able to apply your Java skills to a real-world project. Furthermore, you will also gain the practical experience and demonstrate your abilities.
Software Design & Development- This includes the ability to design and develop robust and scalable software solutions using Java technologies. Along with this, you also have to understand the software development methodologies like Agile and Waterfall.
Application Development (Java)- It is necessary to have proficiency in Java programming language. This includes the core concepts, syntax, and libraries. Furthermore, having experience in building various types of applications is also necessary.
Coding & Reviews- This skill includes having strong coding practices along with code readability, maintainability, and efficiency. Furthermore, you should also be able to clean, well-structured code and participate in code reviews.
Gap Analysis- It refers to the process of identifying the discrepancies between existing systems and desired requirements. Furthermore, you also have to assess the feasibility of implementing new features or functionalities.
Onshore & Offshore Coordination- It is necessary to have skills to collaborate effectively with teams located in different geographical regions. Furthermore, you also have to work on managing the communication and ensuring smooth coordination.
Requirement Gathering & Analysis- This skill includes working on eliciting, documenting, and analyzing user requirements. Thus, ensuring that the software tool meets business needs.
Bug Fixing/ Defect Tracking- It is necessary to have the skills in identifying, troubleshooting, and resolving software defects. Along with this, you should also be able to use the tracking tools to manage and prioritize bug fixes.
Unit Testing- This refers to the process of writing and executing unit tests to verify the correctness of individual software components. Along with this, it also includes ensuring code quality and maintainability.
System Integration Testing- This practice consists of testing the integration of multiple software components and systems. Its primary aim is to ensure they work together as expected.
Access Specifiers: This skill is useful for understanding the public, private, protected, and default access modifiers in Java. Along with this, it helps in understanding how these modifiers affect the visibility of classes, methods, and variables.
Exceptions: It provides you with the knowledge of exception-handling mechanisms in Java. Along with this, it also helps in understanding the different types of exceptions and best practices for handling them.
Generics: Having proficiency in using generics will help you create type-safe code and improve the code reusability. Furthermore, it helps in understanding of type parameters, type inference, and bounded type parameters.
Java Keywords: It is necessary to have familiarity with the commonly used Java keywords like if, else, for, while, switch, case, break, continue, return, and try. Understanding them and their use case will be useful in Java programming.
The OOPs Concepts & Patterns: It is necessary to have a strong grasp of object-oriented programming principles like encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. Technical skills also include design patterns like Singleton, Factory, Etc.
Abstract Classes and Interfaces: This includes an understanding of abstract classes and interfaces and their role in defining contracts and providing code reusability. Java jobs require you to abstract classes and interfaces and implement them in concrete classes.
Constructors: It includes having the knowledge of constructors and their role in initializing objects. Along with this, it is also necessary to have an understanding of default constructors and parameterized constructors.
File IO and Serialization: These skills consist of the ability to read, write, and manipulate files in Java. Along with this, you should also be able to understand the serialization and deserialization mechanisms for persisting objects.
JVM and Memory Management: You should also have knowledge of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and its architecture. Furthermore, it is also necessary to understand garbage collection and memory management in Java.
Multithreading, Concurrency: This skill consists of having proficiency in creating and managing multiple threads in Java. Along with this, you should also have a good understanding of synchronization mechanisms like locks, semaphores, and wait/notify.
Synchronization: This consists of having the knowledge of synchronization techniques to prevent race conditions and ensure thread safety. Along with this, you should also be able to use the synchronized blocks, methods, and atomic operations.
Dependency Injection: You should also be able to understand the dependency injection frameworks like Spring and Guice. This will provide you with the ability to configure dependencies and manage object lifecycles.
SQL Queries: Jobs in Java require proficiency in writing SQL queries as it is useful for interacting with databases. Along with this, you also need to have knowledge of SQL syntax, data types, and common database operations.
Stored Procedures: You should be able to understand stored procedures and their benefits in database programming. Along with this, it is necessary that you create and use stored procedures to encapsulate database logic.
Triggers: This consists of the knowledge of triggers and their use cases in database programming. Furthermore, you should also be able to create and manage triggers to automate database tasks.
JSP / Servlets: You should also be able to understand JSP and Servlets for building web applications. Along with this, jobs in Java also require the knowledge of JSP tags, directives, and scripting elements.
Web Frameworks (Struts, Spring, Hibernate, Wicket): It is necessary to have the skills and experience of popular Java web frameworks. This is useful for building enterprise applications. Along with this, you should also be able to understand their features and benefits.
Service Oriented Architecture: It includes having the knowledge of service-oriented architecture principles and best practices. Furthermore, you should also be able to design and develop microservices-based applications.
HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Jquery: These skills consist of an understanding of front-end technologies for building user interfaces. Along with this, you should also be able to work with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and JQuery.
XML and JSON: The jobs ion Java also require you to have knowledge of XML and JSON data formats. This will showcase your ability to parse and manipulate XML and JSON data.
Java: Java is the backbone of full-stack development, offering developers a versatile, high-level programming language. Its "write once, run anywhere" capability allows applications to be deployed across different platforms seamlessly. Java is widely used to create secure, scalable, and high-performance server-side applications. For a full-stack developer, mastering Java opens doors to a wide range of back-end opportunities.
Spring Boot: Spring Boot is like a power tool for Java developers, making it easier to build modern web applications. It reduces boilerplate code and speeds up development by offering built-in libraries and simplified configuration. With Spring Boot, developers can create microservices or enterprise-level applications in a fraction of the time. Its also great for integrating various technologies smoothly into your project.
Hibernate: Hibernate is your go-to for working with databases in Java, simplifying database operations with minimal effort. It maps Java objects to database tables, meaning you dont have to write complex SQL queries to manage your data. Hibernate streamlines database management and is crucial for efficiently handling large-scale data in full-stack applications. With its flexibility, it supports multiple databases seamlessly.
Apache Maven: Maven is like the project manager for your code, ensuring everything fits together perfectly. It manages your projects dependencies, builds, and deployment processes, keeping the workflow smooth and organized. With Maven, full-stack developers dont have to manually handle external librariesMaven fetches them automatically, ensuring compatibility. This makes it easy to scale and maintain Java applications.
JUnit: JUnit is your safety net in Java development, ensuring that your code works as expected through automated testing. It allows developers to write tests for individual components, catching errors early before they hit production. For full-stack developers, JUnit ensures the reliability of back-end logic, making sure new features or changes dont break existing code. Its essential for maintaining high-quality, bug-free applications.
Git: Git is like the memory of your code, tracking every change you make and letting you go back to previous versions if needed. Its a version control system that works on the same project without conflicts and enables collaboration, allowing multiple developers. Git ensures that all code changes are properly managed, making it a cornerstone for full-stack development teams. It also integrates with platforms like GitHub for better team collaboration.
Jenkins: Jenkins is an automation server that acts like a personal assistant for developers, automating repetitive tasks like building, testing, and deploying code. Its essential for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD), allowing full stack developers to release updates faster and with fewer errors. Jenkins keeps the development pipeline smooth, from writing code to getting it live.
Apache Tomcat: Apache Tomcat is an open-source web server that runs Java-based applications. Its like the engine that drives your web app, handling the deployment of your Java code to the server. For full stack developers, Tomcat offers a reliable platform to host, test, and run applications efficiently. Its lightweight and highly customizable, making it a popular choice for Java-based web services.
MySQL: MySQL is a widely used open-source database that stores and retrieves data for your applications. Its known for its simplicity and speed, making it ideal for full stack developers who need a reliable database solution. Whether youre handling small datasets or scaling up to millions of records, MySQL offers the flexibility and performance needed for modern web applications.
PostgreSQL: PostgreSQL is a powerful, open-source object-relational database system that excels in handling complex queries and large data volumes. Its known for its high extensibility and support for advanced data types, which makes it popular among full stack developers for data-heavy applications. Whether youre dealing with analytics, GIS data, or custom data types, PostgreSQL is a robust choice.
Oracle Database: Oracle Database is an enterprise-grade database management system known for its scalability, reliability, and performance. It offers advanced features like data security, high availability, and automated backups, making it suitable for mission-critical applications. Full stack developers use Oracle for handling complex, large-scale datasets in environments where uptime and data integrity are paramount.
Angular: Angular is a powerful front-end framework used by full stack developers to build dynamic and responsive web applications. It simplifies the development process by providing ready-to-use components, data-binding, and a structured approach to building user interfaces. Angular is particularly useful for creating single-page applications (SPAs), delivering a seamless and interactive user experience.
React: React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces, particularly single-page applications where data needs to change dynamically. It simplifies the creation of interactive elements on a website, making it ideal for full stack developers focused on the front end. Reacts component-based architecture allows developers to build reusable code, improving both efficiency and scalability in large applications.
Bootstrap: Bootstrap is a front-end framework that makes web design faster and easier, offering pre-built components like buttons, forms, and navigation bars. Its a favorite among full stack developers because it ensures that websites are responsive and look good across all devices. With Bootstrap, developers can focus more on functionality without worrying about design inconsistencies.
HTML/CSS: HTML structures your content, while CSS styles it, ensuring that web pages are visually appealing and user-friendly. For full stack developers, mastering HTML/CSS is critical for creating a polished front-end experience that complements the back-end logic of applications. These technologies are essential for building the visual layer of a full stack project.
JavaScript: JavaScript is the language that makes web pages interactive, allowing users to engage with dynamic elements like forms, sliders, and animations. For full stack developers, JavaScript bridges the gap between the front end and back end, ensuring seamless interaction between the user and the server. Its an essential skill for building modern, responsive web applications.
Docker: Docker simplifies the deployment process by packaging applications and their dependencies into containers, ensuring they run consistently across different environments. For full stack developers, Docker allows for easy setup and scaling of applications, making development, testing, and production smoother. It eliminates the "it works on my machine" problem, ensuring your app works the same everywhere.
Kubernetes: Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that manages the deployment, scaling, and operations of application containers across clusters of hosts. For full-stack developers, Kubernetes automates much of the complexity involved in managing containerized applications, making it easier to scale services and ensure high availability. Its crucial for running large-scale, cloud-native applications stably and efficiently.
Redis: Redis is a data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker in an in-memory structure. Its known for its speed and flexibility, allowing full stack developers to enhance application performance, particularly for real-time data processing. Redis is ideal for storing frequently accessed data, ensuring rapid retrieval, and reducing the load on traditional databases.
Elasticsearch: Elasticsearch is a distributed search and analytics engine that quickly finds and analyzes large volumes of data. Its particularly useful for applications that need real-time search capabilities, such as e-commerce sites or log management systems. Full-stack developers use Elasticsearch to improve search performance, allowing users to retrieve relevant data faster, even from massive datasets.
Java Full Stack Developer- These professionals are responsible for designing, developing, and maintaining web applications' front-end and back-end using Java technologies. They also work with various frameworks and tools, such as Spring, Hibernate, and JavaScript, to create complete web solutions.
Full Stack Java Engineer- Their job role is similar to a full-stack Java developer and they are responsible for handling both front-end and back-end development. Along with it, this job role requires a strong understanding of Java along with the front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
Java Backend Developer- As a Java backend developer, you will be responsible for managing the server-side logic and infrastructure of web applications. These professionals work on platforms like Spring Boot to build APIs and implement business logic.
Frontend Developer with Java Expertise- As a front-end developer with Java Expertise, you will be responsible for showcasing your Java expertise and working on Java-based front-end frameworks. Along with this, these professionals have to work on creating user-friendly and visually appealing interfaces.
Java Microservices Developer- The primary job role of these professionals is to work on building and maintaining small, independent services. Along with this, these professionals also work on Java frameworks like Spring Boot and Spring Cloud to design and implement microservices architecture.
Java DevOps Engineer- Their primary job role is to A Java DevOps engineer combines development and operations skills to automate and streamline the software development lifecycle. They use Java tools and technologies to build, test, deploy, and manage Java-based applications.
Java Cloud Engineer- These professionals have to specialise in designing, developing, and deploying Java applications on cloud platforms. Along with this, these professionals also work on cloud-native technologies and best practices to build scalable and reliable applications.
Java Technical Lead- Their primary job role is to guide and mentor various Java developers. Along with this, they also have to oversee the project development. Along with this, they also ensure code quality and provide businesses with technical expertise.
Java Software Architect- As a Java software architect, you will be primarily responsible for designing and defining the overall structure and architecture of Java-based applications. Along with this, these professionals also make high-level decisions about technology choices, design patterns, and scalability.
Java Spring Developer- As a Java Spring developer, your primary job role will be using the Spring framework to build enterprise-grade Java applications. Along with this, these professionals also work on various Spring modules like Spring Boot, Spring MVC, and Spring Data.
MEAN Stack Developer: Here you will be learning about the MEAN stack which includes MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js. This stack is useful for building dynamic web applications. Along with this, the course will help you gain expertise in JavaScript technologies and their integration.
Python Django Full Stack Developer Course: In the Python Django Ful stack development training, you will master Python and Django for building efficient and scalable web applications. Along with this, you will also learn about database management, web frameworks, and API development.
MERN Stack Developer Course: Enrolling in this course will help you acquire skills in MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js for modern web development. Along with this, you will also focus on building component-based and scalable applications.
Java Full Stack Developer Training: This training covers concepts such as Java, Spring Framework, and other technologies for managing enterprise-level web development. It will further help you develop robust and scalable applications using Java's capabilities.
Django Full Stack Developer: In this training, you will specialize in Django for rapid web development and efficient workflows. Along with this, you will also learn Python, Django, and related technologies for building web applications.
React Full Stack Developer: In this training, you will be learning how to Master React for building dynamic user interfaces and server-side rendering. Along with this, you will learn how to integrate React with back-end technologies for full-stack.
React Native Full Stack Course: Here you will be developing cross-platform mobile apps using React Native. Along with this, you will learn how to build native-like mobile experiences for iOS and Android.
Node JS Full Stack Developer Course: In this training course, you will learn Node.js to build scalable and real-time web applications. Along with this, you will be learning event-driven programming and asynchronous operations.
PHP Full Stack Developer Course: By enrolling in the PHP Full stack developer training, you will acquire skills in PHP, a popular language for web development. Furthermore, you will also learn how to build dynamic websites and web applications using PHP.
Microsoft .NET Full Stack Developer: Along with this, you will be mastering the .NET framework for building web applications within the Microsoft ecosystem. Furthermore, you will learn C#, ASP.NET, and other relevant technologies.
Python Full Stack Developer Course: In this course, you will be gaining Python full stack development skills and receiving career placement assistance. Along with this, you will also learn Python, Django, and other relevant technologies.
Go to the Official Java Website:
Select Java Version:
Download the Installer:
Accept License Agreement:
Run the Installer:
Verify Installation:
Java Full Stack Developer:
Full Stack Java Engineer:
Java Backend Developer:
Frontend Developer with Java Expertise:
Java Microservices Developer:
Java DevOps Engineer:
Java Cloud Engineer:
Java Technical Lead:
Java Software Architect:
Java Spring Developer:
Full Stack Developers are generally the undisputed disciplinary knowledge that can overcome the new trends in the technology sector.
There are multiple job options available in this sector that can appease our new joiners as well as the customers.
Full stack developers help out in reducing our operational costs which can alter out more savings for the customers.
They can organize or reorganize the facilitation procedure of employees on behalf of other persons working in the organization.
This technology in the IT sector will help out in revamping new proceedings about comprising.
The web development technology which allows the handling of both front-end & back-end proceedings must consider the stimulation.
With changing & evolving technologies it becomes easy to hamper & learn new methodologies of consistency.
According to the recent research reports the salary prospects of Java Full Stack Developer can go through the prospects of 16 lakh per annum.
With ongoing right skills & competency, we can also get solitude in the happenings of trends as well as qualities.
It is important to get one-to-one handling as well as a new procedure which we are linking towards them.
Working with the development teams for further reconciliation.
Designing out the multiple client-server side applications.
Handling out the new procedure of handling development.
Becoming adept with new technologies that can help businesses.
Making out more turnovers in & around the organization.
we train you to get hired.

By registering here, I agree to Croma Campus Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy
Course Design By

Nasscom & Wipro
Course Offered By

Croma Campus

Stories
success
inspiration

career upgrad

career upgrad


career upgrad


career upgrad
05-Jul-2025*
07-Jul-2025*
02-Jul-2025*
05-Jul-2025*
07-Jul-2025*
02-Jul-2025*

You will get certificate after
completion of program

You will get certificate after
completion of program

You will get certificate after
completion of program
in Collaboration with






Empowering Learning Through Real Experiences and Innovation
we train you to get hired.
Phone (For Voice Call):
+91-971 152 6942WhatsApp (For Call & Chat):
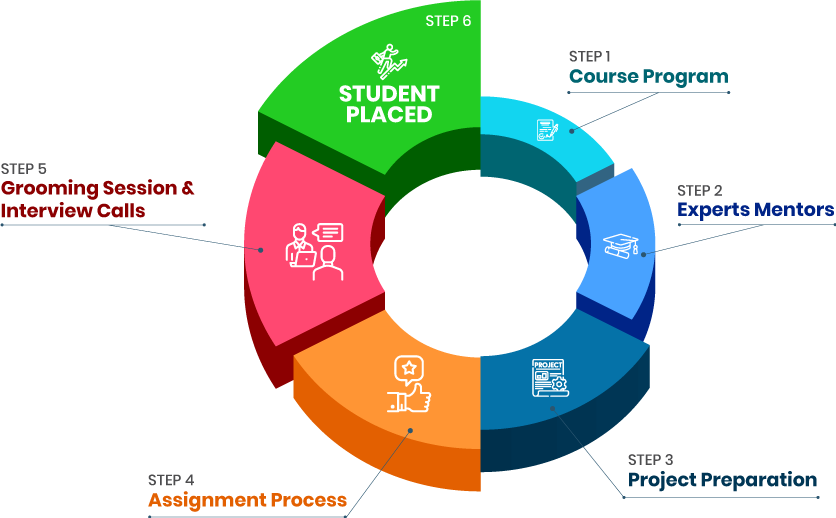
+91-971 152 6942Get a peek through the entire curriculum designed that ensures Placement Guidance
Course Design By


Course Offered By

Ready to streamline Your Process? Submit Your batch request today!
You have just to get through the proceedings of multiple variants to get about Java Full Stack.
Yes, it will assist in learning new methodologies for the enhancement of proceedings.
There are multiple types of full stacks are in demand that can accelerate new happenings.
No, it is not soo hard to learn there are some specifications which we can get the target.
Moreover, there are multiple choices that we can get out but the prominent ones are Spring, React, Apache Spark, etc.
CI/CD enhances Java Full Stack projects by automating code integration, testing, and deployment, ensuring faster and more reliable software delivery. It helps detect bugs early, improves collaboration, and maintains a consistent development workflow. By streamlining deployments and reducing manual errors, CI/CD increases efficiency, enhances software quality, and ensures seamless updates with minimal downtime.
CI/CD makes Java Full Stack Development faster and more efficient by automating build, testing, and deployment. Maven and Gradle manage dependencies, while Jenkins and GitHub Actions handle code integration. Docker and Kubernetes help with smooth and scalable deployments. Spring Boot further simplifies the process with built-in servers and auto-configuration, ensuring reliable and hassle-free development.

FOR QUERIES, FEEDBACK OR ASSISTANCE
Best of support with us
For Voice Call
+91-971 152 6942For Whatsapp Call & Chat
+91-9711526942